What is a timing belt failure?
Timing belts have the ability to transmit power synchronously. Therefore, not only the inability to transmit power, but the loss of synchronous power transmission is considered a failure. The former, it is classified as "breakage" and the latter, is as "tooth chipping" in this page.
In addition to these, there are other issues such as “tooth wear”, where the belt teeth become worn, and “cracks” that appear at the base of the teeth or on the back of the belt. However, these are considered intermediate stages that may eventually lead to breakage or tooth chipping. In other words, progressive tooth wear or the development of cracks at the tooth root or belt back can ultimately result in more severe failures like breakage or tooth chipping.
Causes of timing belt failure
The following are the causes of timing belt failure.
(1) What is Belt "Breakage"?
The direct causes of belt "breakage" are "excessive damage to the cord" and "insufficient strength of the cord". Here are some of the factors that can cause each of these.
➀ Factors of "excessive damage to the cord"
・When tooth skipping is repeated due to overloading
・When overload or tooth skipping occurs repeatedly due to a sudden stop (shock load)
・Repeated tooth skipping due to insufficient tension
・When the pulley rides up on the pulley flange due to insufficient alignment adjustment
② "Insufficient strength of cord" factor
・When the minimum pulley diameter is less than the specified minimum pulley diameter
・When multiple axis loads are not taken into consideration during design
・When the speed is faster than the speed used in the design calculation
・When used in an environment where the belt is directly exposed to water or in a high humidity environment (*in case of glass cord)
(2) What is "tooth chipping" in the belt?
Tooth chipping in belts progresses from root cracks, tooth wear, and bottom tooth wear. The factors behind each of these are listed below.
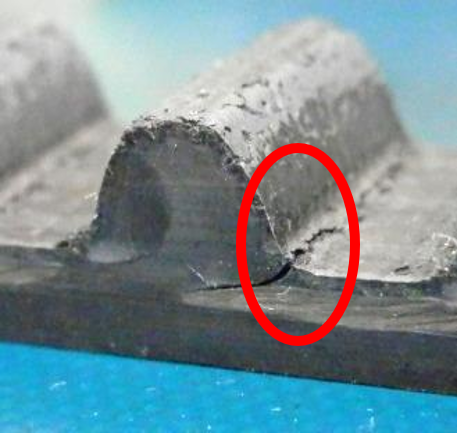

Causes of Root Cracks (*1)
(*1... Refers to cracks that occur at the base of the belt teeth)
・When teeth jump repeatedly due to overloading
・If repeated overloading or tooth skipping occurs due to sudden stopping (shock loading)
・When a belt that is not designed for a high-temperature environment is used in a high-temperature environment
・When the pulley diameter of the rear idler is smaller than that used in the design calculation
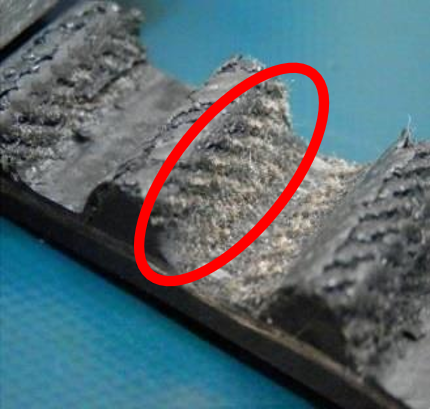
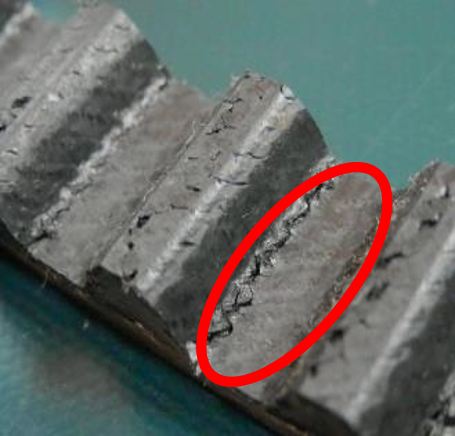
Causes of Tooth Wear (*2)
(*2...the teeth of the belt are worn out and worn away)
・When the number of meshing teeth between the pulley and belt is small, the load on each belt tooth is too high
・When the belt tension is insufficient
・When the pulley surface is rough
・When dust is trapped in the belt

Causes of Tooth Bottom Abrasion (*3)
(*3...Wear and tear on the bottom of the belt teeth)
・When the tooth bottom surface pressure is high due to excessive tension
・When the pulley surface is rough
・When dust is trapped in the belt
Countermeasures Against Timing Belt Failure
This section introduces countermeasures in various causes and cases of timing belt failure.
By monitoring the condition of a belt, it is possible to identify signs of wear and infer potential causes of failure. Taking proactive measures based on these observations can help prevent premature damage and extend the operational life of the equipment.
It is important to remember that belts are consumable components. Over time, they naturally degrade, and issues such as breakage or tooth loss may occur as they reach the end of their service life. To avoid unexpected equipment downtime due to sudden belt failure, it is crucial to replace belts before such problems arise.
Regular visual inspections are highly recommended to detect early signs of deterioration, including tooth root cracks, tooth surface wear, and wear at the base of the teeth. At Bando Chemical Industries, we provide recommended replacement guidelines based on the progression of these wear indicators. The replacement timing is categorized as "C-rank" in the table below, which serves as a reference for determining the appropriate maintenance schedule.
